Drug combinations
WARNING! For educational purposes: We do not endorse any of these combinations. This page will always be 'work in progress'. It is extremely important to be safe at all times! See below the graphic for important information regarding specific combinations.
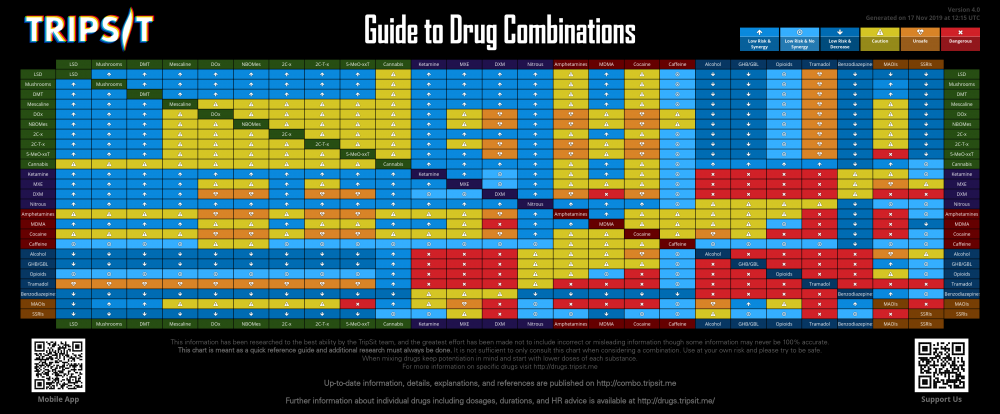
Overview
This chart is meant as a quick reference guide and additional research MUST always be done. If you use this chart or information on your site you must link to the full summaries and display this message.
If you want to give us some feedback/recommendation/comment on the chart, you can contact us:
We have a printed combo chart available here. We also offer a tool to generate a custom sized version of the chart that fits your need via a Github application which you can then take to your local printing place. If you chose to print your own we request that you please donate to help us cover running cost and develop new useful tools. Do note if you wish to edit the chart to your fitting please get in contact with us first via the email below. Printing and reselling the posters is not permitted without explicit written permission via email.
Email: [email protected].
Categorisations
Low Risk & Synergy - These drugs work together to cause an effect greater than the sum of its parts, and they aren't likely to cause an adverse or undesirable reaction when used carefully. Additional research should always be done before combining drugs.
Low Risk & No Synergy - Effects are just additive. The combination is unlikely to cause any adverse or undesirable reaction beyond those that might ordinarily be expected from these drugs.
Caution - These combinations are not usually physically harmful, but may produce undesirable effects, such as physical discomfort or overstimulation. Extreme use may cause physical health issues. Synergistic effects may be unpredictable. Care should be taken when choosing to use this combination.
Unsafe - There is considerable risk of physical harm when taking these combinations, they should be avoided where possible.
Dangerous - These combinations are considered extremely harmful and should always be avoided. Reactions to these drugs taken in combination are highly unpredictable and have a potential to cause death.
Chart versions
Portuguese (Needs Translation)
Polish (Needs Translation)
Use & Attribution
Use of the data the combination chart and app are built upon is free-of-charge for non-commercial purposes. Distribution and display of the combination chart is also free for non-commercial purposes. In both cases, we only require that you link back to either this page, or [1]. This should be accompanied with a note citing TripSit as the source for the information wherever it appears. The presentation should also include a note that the information is only intended for a quick overview and reference, and that it is necessary for users to perform more individual research before making a decision.
Specific Combinations
cannabis & lsd
Status: Caution
Note: Cannabis has an unexpectedly strong and somewhat unpredictable synergy with psychedelics.
amphetamines & lsd
Status: Caution
Note: Stimulants increase anxiety levels and the risk of thought loops which can lead to negative experiences
cocaine & lsd
Status: Caution
Note: Stimulants increase anxiety levels and the risk of thought loops which can lead to negative experiences
tramadol & lsd
Status: Unsafe
Note: Tramadol is well known to lower seizure threshold and psychedelics also cause occasional seizures.
cannabis & mushrooms
Status: Caution
Note: Cannabis has an unexpectedly strong and somewhat unpredictable synergy with psychedelics.
amphetamines & mushrooms
Status: Caution
Note: Stimulants increase anxiety levels and the risk of thought loops which can lead to negative experiences
cocaine & mushrooms
Status: Caution
Note: Stimulants increase anxiety levels and the risk of thought loops which can lead to negative experiences
tramadol & mushrooms
Status: Unsafe
Note: Tramadol is well known to lower seizure threshold and psychedelics also cause occasional seizures.
cannabis & dmt
Status: Caution
Note: Cannabis has an unexpectedly strong and somewhat unpredictable synergy with psychedelics.
amphetamines & dmt
Status: Caution
Note: Stimulants increase anxiety levels and the risk of thought loops which can lead to negative experiences
cocaine & dmt
Status: Caution
Note: Stimulants increase anxiety levels and the risk of thought loops which can lead to negative experiences
tramadol & dmt
Status: Unsafe
Note: Tramadol is well known to lower seizure threshold and psychedelics also cause occasional seizures.
5-meo-xxt & mescaline
Status: Caution
Note: The 5-MeO class of tryptamines can be unpredictable in their interactions
cannabis & mescaline
Status: Caution
Note: Cannabis has an unexpectedly strong and somewhat unpredictable synergy with psychedelics.
amphetamines & mescaline
Status: Caution
Note: The focus and anxiety caused by stimulants is magnified by psychedelics and results in an increased risk of thought loops
cocaine & mescaline
Status: Caution
Note: The focus and anxiety caused by stimulants is magnified by psychedelics and results in an increased risk of thought loops
caffeine & mescaline
Status: Low Risk & No Synergy
Note: High doses of caffeine are uncomfortable and this will be magnified by psychedelics
tramadol & mescaline
Status: Unsafe
Note: This combination can cause seizures due to the lowering of the threshold by tramadol and the potential of mescaline to cause seziures.
5-meo-xxt & dox
Status: Caution
Note: The 5-MeO class of tryptamines can be unpredictable in their interactions, particularly increasing the risk of unpleasant physical side effects.
cannabis & dox
Status: Caution
Note: Cannabis has an unexpectedly strong and somewhat unpredictable synergy with psychedelics.
ketamine & dox
Status: Low Risk & Synergy
Note: Ketamine and psychedelics tend to potentiate each other - go slowly.
mxe & dox
Status: Caution
Note: As an NMDA antagonist MXE potentiates DOx which can be unpleasantly intense
dxm & dox
Status: Unsafe
Note: The DOx class as psychedelic stimulants have the potential to mask the effects of DXM and could lead to redosing to an unsafe level. DXM can also potentiate DOx resulting in an unpleasantly intense experience.
pcp & dox
Status: Unsafe
Note: Details of this combination are not well understood but PCP generally interacts in an unpredictable manner.
amphetamines & dox
Status: Unsafe
Note: The combined stimulating effects of the two can lead to an uncomfortable body-load, while the focusing effects of amphetamine can easily lead to thought loops. Coming down from amphetamines while the DOx is still active can be quite anxiogenic.
mdma & dox
Status: Caution
Note: The combined stimulating effects of the two can be uncomfortable. Coming down on the MDMA while the DOx is still active can be quite anxiogenic.
cocaine & dox
Status: Unsafe
Note: The combined stimulating effects of the two can lead to an uncomfortable body-load, while the focusing effects of cocaine can easily lead to thought loops. Coming down from cocaine while the DOx is still active can be quite anxiogenic
caffeine & dox
Status: Caution
Note: High doses of caffeine may cause anxiety which is less manageable when tripping, and since both are stimulating it may cause some physical discomfort.
alcohol & dox
Status: Low Risk & Decrease
Note: Drinking on stimulants is risky because the sedative effects of the alcohol are reduced, and these are what the body uses to gauge drunkenness. This typically leads to excessive drinking with greatly reduced inhibitions, high risk of liver damage and increased dehydration. They will also allow you to drink past a point where you might normally pass out, increasing the risk.
opioids & dox
Status: Low Risk & No Synergy
Note: No unexpected interactions.
tramadol & dox
Status: Unsafe
Note: Tramadol is well known to lower seizure threshold and psychedelics also cause occasional seizures.
maois & dox
Status: Caution
Note: MAO-B inhibitors can increase the potency and duration of phenethylamines unpredictably
5-meo-xxt & nbomes
Status: Caution
Note: The 5-MeO class of tryptamines can be unpredictable in their interactions and the NBOMes are known to be unpredictable even alone. This combination is best avoided
cannabis & nbomes
Status: Caution
Note: Cannabis has an unexpectedly strong and somewhat unpredictable synergy with psychedelics.
mxe & nbomes
Status: Caution
Note: As an NMDA antagonist MXE potentiates NBOMes which can be unpleasantly intense
amphetamines & nbomes
Status: Unsafe
Note: Amphetamines and NBOMes both provide considerable stimulation. When combined they can result in tachycardia, hypertension, vasoconstriction and in extreme cases heart failure. The anxiogenic and focusing effects of stimulants are also not good in combination with psychedelics as they can lead to unpleasant thought loops. NBOMes are known to cause seizures and stimulants can increase this risk.
cocaine & nbomes
Status: Unsafe
Note: Cocaine and NBOMes both provide considerable stimulation. When combined they can result in severe vasoconstriction, tachycardia, hypertension, and in extreme cases heart failure.
caffeine & nbomes
Status: Caution
Note: Caffiene can bring out the natural stimulation from psychedelic drugs to make it uncomfortable. High doses can cause anxiety which is hard to handle while tripping
tramadol & nbomes
Status: Unsafe
Note: Tramadol is well known to lower seizure threshold and NBOMes have also shown a tendency to cause severe seizures
maois & nbomes
Status: Caution
Note: MAO-B inhibitors can increase the potency and duration of phenethylamines unpredictably
5-meo-xxt & 2c-x
Status: Caution
Note: The 5-MeO psychedelics can interact unpredictably to potentiate other psychedelics
cannabis & 2c-x
Status: Caution
Note: Cannabis has an unexpectedly strong and somewhat unpredictable synergy with psychedelics.
amphetamines & 2c-x
Status: Caution
Note: The anxiogenic and focusing effects of stimulants increase the chance of unpleasant thought loops. The combination is generally uneccessary because of the stimulating effects of psychedelics. Combination of the stimulating effects may be uncomfortable.
cocaine & 2c-x
Status: Caution
Note: The anxiogenic and focusing effects of stimulants increase the chance of unpleasant thought loops. The combination is generally unnecessary because of the stimulating effects of psychedelics. Combination of the stimulating effects may be uncomfortable.
caffeine & 2c-x
Status: Low Risk & No Synergy
Note: High doses of caffeine may cause anxiety which is less manageable when tripping, and since both are stimulating the combination may cause some physical discomfort.
tramadol & 2c-x
Status: Unsafe
Note: Tramadol is well known to lower seizure threshold and psychedelics raise the risk of seizures.
maois & 2c-x
Status: Caution
Note: MAO-B inhibitors can increase the potency and duration of phenethylamines unpredictably
5-meo-xxt & 2c-t-x
Status: Caution
Note: Both classes of compounds can be unpredictable alone
cannabis & 2c-t-x
Status: Caution
Note: Cannabis has an unexpectedly strong and somewhat unpredictable synergy with psychedelics.
amphetamines & 2c-t-x
Status: Unsafe
Note: Stimulants increase anxiety levels and the risk of thought loops which can lead to negative experiences. In extreme cases, they can result in severe vasoconstriction, tachycardia, hypertension, and in extreme cases heart failure.
cocaine & 2c-t-x
Status: Unsafe
Note: Cocaine and 2c-t-x both provide considerable stimulation. When combined they can result in severe vasoconstriction, tachycardia, hypertension, and in extreme cases heart failure.
caffeine & 2c-t-x
Status: Low Risk & No Synergy
Note: High doses of caffeine may cause anxiety which is less manageable when tripping, and since both are stimulating the combination may cause some physical discomfort.
alcohol & 2c-t-x
Status: Low Risk & Decrease
Note: Both these classes of compound can interact unpredictably. Caution should be exercised.
opioids & 2c-t-x
Status: Low Risk & No Synergy
Note: No expected interactions, some opioids have serotonin action, and could lead to Serotonin Syndrome or a seizure. These are pretty much only to Pentazocine, Methadone, Tramadol, Tapenatdol.
maois & 2c-t-x
Status: Caution
Note: MAO-B inhibitors can increase the potency and duration of phenethylamines unpredictably, which could be dangerous given the unpredictability of the 2C-T-x series
cannabis & amt
Status: Caution
Note: Cannabis has an unexpectedly strong and somewhat unpredictable synergy with psychedelics. Small amounts can reduce nausea with aMT but take care.
caffeine & amt
Status: Caution
Note: High doses of caffeine may cause anxiety which is less manageable when tripping, and since both are stimulating the combination may cause some physical discomfort.
alcohol & amt
Status: Caution
Note: aMT has a broad mechanism of action in the brain and so does alcohol so the combination can be unpredictable
opioids & amt
Status: Low Risk & No Synergy
Note: No unexpected interactions
maois & amt
Status: Dangerous
Note: aMT is an MAOI on its own. Using enzyme inhibitors can greatly reduce predictability of effects.
mxe & 5-meo-xxt
Status: Low Risk & Synergy
Note: Little information exists about this combination.
dxm & 5-meo-xxt
Status: Unsafe
Note: Little information exists about this combination.
cannabis & 5-meo-xxt
Status: Caution
Note: Cannabis has an unexpectedly strong and somewhat unpredictable synergy with psychedelics.
amphetamines & 5-meo-xxt
Status: Unsafe
Note: The anxiogenic and focusing effects of stimulants increase the chance of unpleasant thought loops. The combination is generally unnecessary because of the stimulating effects of psychedelics.
mdma & 5-meo-xxt
Status: Caution
Note: Some of the 5-MeO tryptamines are a bit unpredictable and should be mixed with MDMA with care
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28677880 ; Just in case I forget.
cocaine & 5-meo-xxt
Status: Unsafe
Note: The anxiogenic and focusing effects of stimulants increase the chance of unpleasant thought loops. The combination is generally unnecessary because of the stimulating effects of psychedelics.
caffeine & 5-meo-xxt
Status: Low Risk & No Synergy
Note: High doses of caffeine may cause anxiety which is less manageable when tripping, and since both are stimulating the combination may cause some physical discomfort.
amphetamines & cannabis
Status: Caution
Note: Stimulants increase anxiety levels and the risk of thought loops which can lead to negative experiences
mdma & cannabis
Status: Low Risk & Synergy
Note: Large amounts of either or both may cause strong and somewhat unpredictable experiences, which can be as intense as psychedelics. Consider rather Set and Setting are good, before you combine these. Cannabis should be saved for towards the end of the MDMA experience if possible, where the psychedelic alike effect won't come to play.
cocaine & cannabis
Status: Caution
Note: Stimulants increase anxiety levels and the risk of thought loops which can lead to negative experiences
alcohol & cannabis
Status: Low Risk & Synergy
Note: In excess, this combination can cause nausea.
amphetamines & ketamine
Status: Caution
Note: No unexpected interactions, though likely to increase blood pressure but not an issue with sensible doses. Moving around on high doses of this combination may be ill advised due to risk of physical injury.
mdma & ketamine
Status: Low Risk & Synergy
Note: No unexpected interactions, though likely to increase blood pressure but not an issue with sensible doses. Moving around on high doses of this combination may be ill advised due to risk of physical injury.
cocaine & ketamine
Status: Caution
Note: No unexpected interactions, though likely to increase blood pressure but not an issue with sensible doses. Moving around on high doses of this combination may be ill advised due to risk of physical injury.
caffeine & ketamine
Status: Low Risk & No Synergy
Note: No unexpected interactions.
alcohol & ketamine
Status: Dangerous
Note: Both substances cause ataxia and bring a very high risk of vomiting and unconsciousness. If the user falls unconscious while under the influence there is a severe risk of vomit aspiration if they are not placed in the recovery position.
ghb/gbl & ketamine
Status: Dangerous
Note: Both substances cause ataxia and bring a risk of vomiting and unconsciousness. If the user falls unconscious while under the influence there is a severe risk of vomit aspiration if they are not placed in the recovery position.
opioids & ketamine
Status: Dangerous
Note: Both substances bring a risk of vomiting and unconsciousness. If the user falls unconscious while under the influence there is a severe risk of vomit aspiration if they are not placed in the recovery position.
benzodiazepines & ketamine
Status: Caution
Note: Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position.
maois & ketamine
Status: Caution
Note: MAO-B inhibitors appear to increase the potency of Ketamine. MAO-A inhbitors have some negative reports associated with the combination but there isn't much information available
pcp & mxe
Status: Caution
Note: There are no reports available about this combination
amphetamines & mxe
Status: Caution
Note: Risk of tachycardia, hypertension, and manic states
mdma & mxe
Status: Caution
Note: There have been reports of risky serotonergic interactions when the two are taken at the same time, but MXE taken to the end of an MDMA experience does not appear to cause the same issues.
cocaine & mxe
Status: Caution
Note: Stimulants taken with MXE can lead to hypermanic states much more easily, especially if sleep is avoided.
caffeine & mxe
Status: Low Risk & No Synergy
Note: No likely interactions
alcohol & mxe
Status: Dangerous
Note: There is a high risk of memory loss, vomiting and severe ataxia from this combination.
ghb/gbl & mxe
Status: Dangerous
Note: Both substances cause ataxia and bring a risk of vomiting and unconsciousness. If the patient falls unconscious while under the influence there is a severe risk of vomit aspiration if they are not placed in the recovery position.
opioids & mxe
Status: Dangerous
Note: This combination can potentiate the effects of the opioid
benzodiazepines & mxe
Status: Caution
Note: Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. Place affected patients in the recovery position to prevent vomit aspiration from excess.
maois & mxe
Status: Unsafe
Note: MAO-B inhibitors appear to increase the potency of MXE. MAO-A inhbitors have some negative reports associated with the combination but there isn't much information available
ssris & mxe
Status: Caution
Note: Depending on the SSRI this combination can be unpredictable
amphetamines & dxm
Status: Unsafe
Note: Both substances raise heart rate, in extreme cases, panic attacks caused by these drugs have led to more serious heart issues.
cocaine & dxm
Status: Unsafe
Note: Both substances raise heart rate, in extreme cases, panic attacks caused by these drugs have led to more serious heart issues
caffeine & dxm
Status: Low Risk & No Synergy
Note: High doses of caffeine may cause anxiety which is less manageable when tripping, and since both are stimulating the combination may cause some physical discomfort.
alcohol & dxm
Status: Dangerous
Note: Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. Place affected patients in the recovery position to prevent vomit aspiration from excess. Additionally CNS depression can lead to difficulty breathing. Avoid on anything higher than 1st plateau.
ghb/gbl & dxm
Status: Dangerous
Note: Both substances cause ataxia and bring a risk of vomiting and unconsciousness. If the patient falls unconscious while under the influence there is a severe risk of vomit aspiration if they are not placed in the recovery position. This combination is hard to predict
opioids & dxm
Status: Dangerous
Note: CNS depression, difficult breathing, heart issues, hepatoxic, just very unsafe combination all around. Additionally if one takes dxm, their tolerance of opiates goes down slightly, thus causing additional synergistic effects.
benzodiazepines & dxm
Status: Caution
Note: Small doses of benzos can end a bad trip, but both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and this can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position.
maois & dxm
Status: Dangerous
Note: High risk of serotonin syndrome
ssris & dxm
Status: Dangerous
Note: High risk of serotonin syndrome.
amphetamines & pcp
Status: Unsafe
Note: This combination can easily lead to hypermanic states
mdma & pcp
Status: Unsafe
Note: This combination can easily lead to hypermanic states
cocaine & pcp
Status: Unsafe
Note: This combination can easily lead to hypermanic states
caffeine & pcp
Status: Caution
Note: Details of this combination are not well understood but PCP generally interacts in an unpredictable manner.
alcohol & pcp
Status: Unsafe
Note: Details of this combination are not well understood but PCP generally interacts in an unpredictable manner.
ghb/gbl & pcp
Status: Dangerous
Note: Details of this combination are not well understood but PCP generally interacts in an unpredictable manner.
opioids & pcp
Status: Caution
Note: PCP can reduce opioid tolerance, increasing the risk of overdose
benzodiazepines & pcp
Status: Unsafe
Note: Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position. Memory blackouts are likely
maois & pcp
Status: Dangerous
Note: This combination is very poorly explored
ssris & pcp
Status: Unsafe
Note: Details of this combination are not well understood but PCP generally interacts in an unpredictable manner.
alcohol & nitrous
Status: Caution
Note: Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position. Memory blackouts are likely.
ghb/gbl & nitrous
Status: Caution
Note: Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position. Memory blackouts are likely.
opioids & nitrous
Status: Caution
Note: Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position. Memory blackouts are likely.
tramadol & nitrous
Status: Caution
Note: Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position. Memory blackouts are likely.
mdma & amphetamines
Status: Low Risk & Synergy
Note: Amphetamines increase the neurotoxic effects of MDMA
cocaine & amphetamines
Status: Caution
Note: This combination of stimulants will increase strain on the heart. It is not generally worth it as cocaine has a mild blocking effect on dopamine releasers like amphetamine
caffeine & amphetamines
Status: Caution
Note: This combination of stimulants is not generally necessary and may increase strain on the heart, as well as potentially causing anxiety and greater physical discomfort.
alcohol & amphetamines
Status: Caution
Note: Drinking on stimulants is risky because the sedative effects of the alcohol are reduced, and these are what the body uses to gauge drunkenness. This typically leads to excessive drinking with greatly reduced inhibitions, high risk of liver damage and increased dehydration. They will also allow you to drink past a point where you might normally pass out, increasing the risk. If you do decide to do this then you should set a limit of how much you will drink each hour and stick to it, bearing in mind that you will feel the alcohol and the stimulant less. Extended release formulations may severely impede sleep, further worsening the hangover.
ghb/gbl & amphetamines
Status: Caution
Note: Stimulants increase respiration rate allowing a higher dose of sedatives. If the stimulant wears off first then the opiate may overcome the patient and cause respiratory arrest.
opioids & amphetamines
Status: Caution
Note: Stimulants increase respiration rate allowing a higher dose of opiates. If the stimulant wears off first then the opiate may overcome the patient and cause respiratory arrest.
tramadol & amphetamines
Status: Dangerous
Note: Tramadol and stimulants both increase the risk of seizures.
benzodiazepines & amphetamines
Status: Low Risk & Decrease
Note: Both can dull each other's effects, so if one wears off before the other it's possible to overdose due to the lack of counteraction
maois & amphetamines
Status: Dangerous
Note: MAO-B inhibitors can increase the potency and duration of phenethylamines unpredictably. MAO-A inhibitors with amphetamine can lead to hypertensive crises.
cocaine & mdma
Status: Caution
Note: Cocaine blocks some of the desirable effects of MDMA while increasing the risk of heart attack.
caffeine & mdma
Status: Caution
Note: Caffiene is not really necessary with MDMA and increases any neurotoxic effects from MDMA
alcohol & mdma
Status: Caution
Note: Both MDMA and alcohol cause dehydration. Approach this combination with caution, moderation and sufficient hydration. More than a small amount of alcohol will dull the euphoria of MDMA
ghb/gbl & mdma
Status: Caution
Note: Large amounts of GHB/GBL may overwhelm the effects of MDMA on the comedown.
tramadol & mdma
Status: Dangerous
Note: Tramadol and stimulants both increase the risk of seizures.
maois & mdma
Status: Dangerous
Note: MAO-B inhibitors can increase the potency and duration of phenethylamines unpredictably. MAO-A inhibitors with MDMA will lead to hypertensive crises.
caffeine & cocaine
Status: Caution
Note: Both stimulants, risk of tachycardia, hypertension, and in extreme cases heart failure.
alcohol & cocaine
Status: Unsafe
Note: Drinking on stimulants is risky because the sedative effects of the alcohol are reduced, and these are what the body uses to gauge drunkenness. This typically leads to excessive drinking with greatly reduced inhibitions, high risk of liver damage and increased dehydration. They will also allow you to drink past a point where you might normally pass out, increasing the risk. If you do decide to do this then you should set a limit of how much you will drink each hour and stick to it, bearing in mind that you will feel the alcohol less. Cocaine is potentiated somewhat by alcohol because of the formation of cocaethylene.
ghb/gbl & cocaine
Status: Caution
Note: Stimulants increase respiration rate allowing a higher dose of sedatives. If the stimulant wears off first then the opiate may overcome the patient and cause respiratory arrest. Likewise the G can wear off and leave a dangerous concentration of cocaine behind
opioids & cocaine
Status: Dangerous
Note: Stimulants increase respiration rate allowing a higher dose of opiates. If the stimulant wears off first then the opiate may overcome the patient and cause respiratory arrest.
tramadol & cocaine
Status: Dangerous
Note: Tramadol and stimulants both increase the risk of seizures.
maois & cocaine
Status: Dangerous
Note: This combination is poorly explored
ssris & cocaine
Status: Low Risk & No Synergy
Note: May reduce each others' effectiveness. Cocaine can reduce mental stability and therefore exacerbate conditions which SSRIs are used to treat.
ghb/gbl & alcohol
Status: Dangerous
Note: Even in very low doses this combination rapidly leads to memory loss, severe ataxia and unconsciousness. There is a high risk of vomit aspiration while unconscious.
opioids & alcohol
Status: Dangerous
Note: Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. Place affected patients in the recovery position to prevent vomit aspiration from excess. Memory blackouts are likely
tramadol & alcohol
Status: Dangerous
Note: Heavy CNS depressants, risk of seizures. Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. Place affected patients in the recovery position to prevent vomit aspiration from excess. Memory blackouts are likely.
benzodiazepines & alcohol
Status: Dangerous
Note: Ethanol ingestion may potentiate the CNS effects of many benzodiazepines. The two substances potentiate each other strongly and unpredictably, very rapidly leading to unconsciousness. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position. Blacking out and memory loss is almost certain.
maois & alcohol
Status: Unsafe
Note: Tyramine found in many alcoholic beverages can have dangerous reactions with MAOIs, causing an increase in blood pressure.
ssris & alcohol
Status: Caution
Note: Alcohol may potentiate some of the pharmacologic effects of CNS-active agents. Use in combination may result in additive central nervous system depression and/or impairment of judgment, thinking, and psychomotor skills.
opioids & ghb/gbl
Status: Dangerous
Note: The two substances potentiate each other strongly and unpredictably, very rapidly leading to unconsciousness. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position
tramadol & ghb/gbl
Status: Dangerous
Note: The sedative effects of this combination can lead to dangerous respiratory depression.
benzodiazepines & ghb/gbl
Status: Dangerous
Note: The two substances potentiate each other strongly and unpredictably, very rapidly leading to unconsciousness. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position.
tramadol & opioids
Status: Dangerous
Note: Concomitant use of tramadol increases the seizure risk in patients taking other opioids. These agents are often individually epileptogenic and may have additive effects on seizure threshold during coadministration. Central nervous system- and/or respiratory-depressant effects may be additively or synergistically present
benzodiazepines & opioids
Status: Dangerous
Note: Central nervous system and/or respiratory-depressant effects may be additively or synergistically present. The two substances potentiate each other strongly and unpredictably, very rapidly leading to unconsciousness. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position Blackouts/memory loss likely
maois & opioids
Status: Caution
Note: Coadministration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) with certain opioids has been associated with rare reports of severe and fatal adverse reactions. There appear to be two types of interaction, an excitatory and a depressive one. Symptoms of the excitatory reaction may include agitation, headache, diaphoresis, hyperpyrexia, flushing, shivering, myoclonus, rigidity, tremor, diarrhea, hypertension, tachycardia, seizures, and coma. Death has occurred in some cases.
ssris & opioids
Status: Low Risk & No Synergy
Note: There have been very infrequent reports of a risk of serotonin syndrome with this combination, though this should not be a practical concern.
benzodiazepines & tramadol
Status: Dangerous
Note: Central nervous system- and/or respiratory-depressant effects may be additively or synergistically present. Vomit aspiration a risk when passed out, lay down in recovery position if ingested.
--
LSD & Mushrooms
LSD & DMT
LSD & Mescaline
LSD & DOx
LSD & NBOMes
LSD & 2C-x
LSD & 2C-T-x
LSD & αMT
LSD & 5-MeO-xxT
LSD & Cannabis
LSD & Ketamine
LSD & MXE
LSD & DXM
LSD & Nitrous
LSD & Amphetamines
LSD & MDMA
LSD & Cocaine
LSD & Caffeine
LSD & Alcohol
LSD & GHB\GBL
LSD & Opioids
- "Low doses antagonized the effects of both hallucinogens, whereas larger doses enhanced their effects."
LSD & Tramadol
LSD & Benzodiazepines
LSD & MAOIs
LSD & SSRIs
Mushrooms & DMT
Mushrooms & Mescaline
Mushrooms & DOx
Mushrooms & NBOMes
Mushrooms & 2C-x
Mushrooms & 2C-T-x
Mushrooms & αMT
Mushrooms & 5-MeO-xxT
Mushrooms & Cannabis
Mushrooms & Ketamine
Mushrooms & MXE
Mushrooms & DXM
Mushrooms & Nitrous
Mushrooms & Amphetamines
Mushrooms & MDMA
Mushrooms & Cocaine
Mushrooms & Caffeine
Mushrooms & Alcohol
Mushrooms & GHB\GBL
Mushrooms & Opioids
Mushrooms & Tramadol
Mushrooms & Benzodiazepines
Mushrooms & MAOIs
Mushrooms & SSRIs
DMT & Mescaline
DMT & DOx
DMT & NBOMes
DMT & 2C-x
DMT & 2C-T-x
DMT & αMT
DMT & 5-MeO-xxT
DMT & Cannabis
DMT & Ketamine
DMT & MXE
DMT & DXM
DMT & Nitrous
DMT & Amphetamines
DMT & MDMA
DMT & Cocaine
DMT & Caffeine
DMT & Alcohol
DMT & GHB\GBL
DMT & Opioids
DMT & Tramadol
DMT & Benzodiazepines
DMT & MAOIs
DMT & SSRIs
Mescaline & DOx
Mescaline & NBOMes
Mescaline & 2C-x
Mescaline & 2C-T-x
Mescaline & αMT
Mescaline & 5-MeO-xxT
- The 5-MeO class of tryptamines can be unpredictable in their interactions.
Mescaline & Cannabis
Mescaline & Ketamine
Mescaline & MXE
Mescaline & DXM
Mescaline & Nitrous
Mescaline & Amphetamines
- The focus and anxiety caused by stimulants is magnified by psychedelics and results in an increased risk of thought loops.
Mescaline & MDMA
Mescaline & Cocaine
- The focus and anxiety caused by stimulants is magnified by psychedelics and results in an increased risk of thought loops.
Mescaline & Caffeine
- High doses of caffeine are uncomfortable and this will be magnified by psychedelics.
Mescaline & Alcohol
Mescaline & GHB\GBL
Mescaline & Opioids
Mescaline & Tramadol
- This combination can cause seizures due to the lowering of the threshold by tramadol and the potential of mescaline to cause seziures.
Mescaline & Benzodiazepines
Mescaline & MAOIs
Mescaline & SSRIs
DOx & NBOMes
DOx & 2C-x
DOx & 2C-T-x
DOx & αMT
DOx & 5-MeO-xxT
- The 5-MeO class of tryptamines can be unpredictable in their interactions, particularly increasing the risk of unpleasant physical side effects.
DOx & Cannabis
DOx & Ketamine
- Ketamine and psychedelics tend to potentiate each other - go slowly.
DOx & MXE
- As an NMDA antagonist MXE potentiates DOx which can be unpleasantly intense.
DOx & DXM
- The DOx class as psychedelic stimulants have the potential to mask the effects of DXM and could lead to redosing to an unsafe level. DXM can also potentiate DOx resulting in an unpleasantly intense experience.
DOx & Nitrous
DOx & Amphetamines
- The combined stimulating effects of the two can lead to an uncomfortable body-load, while the focusing effects of amphetamine can easily lead to thought loops. Coming down from amphetamines while the DOx is still active can be quite anxiogenic.
DOx & MDMA
- The combined stimulating effects of the two can be uncomfortable. Coming down on the MDMA while the DOx is still active can be quite anxiogenic.
DOx & Cocaine
- The combined stimulating effects of the two can lead to an uncomfortable body-load, while the focusing effects of cocaine can easily lead to thought loops. Coming down from cocaine while the DOx is still active can be quite anxiogenic.
DOx & Caffeine
- High doses of caffeine may cause anxiety which is less manageable when tripping, and since both are stimulating it may cause some physical discomfort.
DOx & Alcohol
- Drinking on stimulants is risky because the sedative effects of the alcohol are reduced, and these are what the body uses to gauge drunkenness. This typically leads to excessive drinking with greatly reduced inhibitions, high risk of liver damage and increased dehydration. They will also allow you to drink past a point where you might normally pass out, increasing the risk.
DOx & GHB\GBL
DOx & Opioids
- No unexpected interactions.
DOx & Tramadol
- Tramadol is well known to lower seizure threshold and psychedelics also cause occasional seizures.
DOx & Benzodiazepines
DOx & MAOIs
DOx & SSRIs
NBOMes & 2C-x
NBOMes & 2C-T-x
NBOMes & αMT
NBOMes & 5-MeO-xxT
- The 5-MeO class of tryptamines can be unpredictable in their interactions and the NBOMes are known to be unpredictable even alone. This combination is best avoided.
NBOMes & Cannabis
NBOMes & Ketamine
NBOMes & MXE
NBOMes & DXM
NBOMes & Nitrous
NBOMes & Amphetamines
- Amphetamines and NBOMes both provide considerable stimulation. When combined they can result in tachycardia, hypertension, vasoconstriction and in extreme cases heart failure. The anxiogenic and focusing effects of stimulants are also not good in combination with psychedelics as they can lead to unpleasant thought loops. NBOMes are known to cause seizures and stimulants can increase this risk.
NBOMes & MDMA
NBOMes & Cocaine
- Cocaine and NBOMes both provide considerable stimulation. When combined they can result in severe vasoconstriction, tachycardia, hypertension, and in extreme cases heart failure.
NBOMes & Caffeine
- Caffiene can bring out the natural stimulation from psychedelic drugs to make it uncomfortable. High doses can cause anxiety which is hard to handle while tripping.
NBOMes & Alcohol
NBOMes & GHB\GBL
NBOMes & Opioids
NBOMes & Tramadol
- Tramadol is well known to lower seizure threshold and NBOMes have also shown a tendency to cause severe seizures.
NBOMes & Benzodiazepines
NBOMes & MAOIs
NBOMes & SSRIs
2C-x & 2C-T-x
2C-x & αMT
2C-x & 5-MeO-xxT
- The 5-MeO psychedelics can interact unpredictably to potentiate other psychedelics.
2C-x & Cannabis
2C-x & Ketamine
2C-x & MXE
2C-x & DXM
2C-x & Nitrous
2C-x & Amphetamines
- The anxiogenic and focusing effects of stimulants increase the chance of unpleasant thought loops. The combination is generally uneccessary because of the stimulating effects of psychedelics. Combination of the stimulating effects may be uncomfortable.
2C-x & MDMA
2C-x & Cocaine
- The anxiogenic and focusing effects of stimulants increase the chance of unpleasant thought loops. The combination is generally unnecessary because of the stimulating effects of psychedelics. Combination of the stimulating effects may be uncomfortable.
2C-x & Caffeine
- High doses of caffeine may cause anxiety which is less manageable when tripping, and since both are stimulating the combination may cause some physical discomfort.
2C-x & Alcohol
2C-x & GHB\GBL
2C-x & Opioids
2C-x & Tramadol
- Tramadol is well known to lower seizure threshold and psychedelics raise the risk of seizures.
2C-x & Benzodiazepines
2C-x & MAOIs
2C-x & SSRIs
2C-T-x & αMT
2C-T-x & 5-MeO-xxT
2C-T-x & Cannabis
2C-T-x & Ketamine
2C-T-x & MXE
2C-T-x & DXM
2C-T-x & Nitrous
2C-T-x & Amphetamines
2C-T-x & MDMA
2C-T-x & Cocaine
2C-T-x & Caffeine
- High doses of caffeine may cause anxiety which is less manageable when tripping, and since both are stimulating the combination may cause some physical discomfort.
2C-T-x & Alcohol
- Both these classes of compound can interact unpredictably. Caution should be exercised.
2C-T-x & GHB\GBL
2C-T-x & Opioids
- No expected interactions, some Opioids have Serotonin action, and could lead to Serotonin Syndrome or a seizure. These are pretty much only to Pentazocine, Methadone, Tramadol, Tapenatdol.
2C-T-x & Tramadol
2C-T-x & Benzodiazepines
2C-T-x & MAOIs
2C-T-x & SSRIs
αMT & 5-MeO-xxT
αMT & Cannabis
αMT & Ketamine
αMT & MXE
αMT & DXM
αMT & Nitrous
αMT & Amphetamines
αMT & MDMA
αMT & Cocaine
αMT & Caffeine
- High doses of caffeine may cause anxiety which is less manageable when tripping, and since both are stimulating the combination may cause some physical discomfort.
αMT & Alcohol
- αMT has a broad mechanism of action in the brain and so does alcohol so the combination can be unpredictable.
αMT & GHB\GBL
αMT & Opioids
- No unexpected interactions
αMT & Tramadol
αMT & Benzodiazepines
αMT & MAOIs
αMT & SSRIs
5-MeO-xxT & Cannabis
5-MeO-xxT & Ketamine
5-MeO-xxT & MXE
5-MeO-xxT & DXM
5-MeO-xxT & Nitrous
5-MeO-xxT & Amphetamines
- The anxiogenic and focusing effects of stimulants increase the chance of unpleasant thought loops. The combination is generally unnecessary because of the stimulating effects of psychedelics.
5-MeO-xxT & MDMA
- Some of the 5-MeO tryptamines are a bit unpredictable and should be mixed with MDMA with care.
5-MeO-xxT & Cocaine
- The anxiogenic and focusing effects of stimulants increase the chance of unpleasant thought loops. The combination is generally unnecessary because of the stimulating effects of psychedelics.
5-MeO-xxT & Caffeine
5-MeO-xxT & Alcohol
5-MeO-xxT & GHB\GBL
5-MeO-xxT & Opioids
5-MeO-xxT & Tramadol
5-MeO-xxT & Benzodiazepines
5-MeO-xxT & MAOIs
5-MeO-xxT & SSRIs
Cannabis & Ketamine
Cannabis & MXE
Cannabis & DXM
Cannabis & Nitrous
Cannabis & Amphetamines
Cannabis & MDMA
Cannabis & Cocaine
Cannabis & Caffeine
Cannabis & Alcohol
Cannabis & GHB\GBL
Cannabis & Opioids
Cannabis & Tramadol
Cannabis & Benzodiazepines
Cannabis & MAOIs
Cannabis & SSRIs
Ketamine & MXE
Ketamine & DXM
Ketamine & Nitrous
Ketamine & Amphetamines
- Amphetamine worsens Ketamines ataxia.
Ketamine & MDMA
Ketamine & Cocaine
Ketamine & Caffeine
- No unexpected interactions.
Ketamine & Alcohol
- Both substances cause ataxia and bring a very high risk of vomiting and unconsciousness. If the user falls unconscious while under the influence there is a severe risk of vomit aspiration if they are not placed in the recovery position.
Ketamine & GHB\GBL
- Both substances cause ataxia and bring a risk of vomiting and unconsciousness. If the user falls unconscious while under the influence there is a severe risk of vomit aspiration if they are not placed in the recovery position.
Ketamine & Opioids
- Both substances bring a risk of vomiting and unconsciousness. If the user falls unconscious while under the influence there is a severe risk of vomit aspiration if they are not placed in the recovery position.
Ketamine & Tramadol
- No unexpected interactions.
Ketamine & Benzodiazepines
- Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position.
Ketamine & MAOIs
Ketamine & SSRIs
MXE & DXM
MXE & Nitrous
MXE & Amphetamines
- Risk of tachycardia, hypertension, and manic states.
MXE & MDMA
- There have been reports of risky serotonergic interactions when the two are taken at the same time, but MXE taken to the end of an MDMA experience does not appear to cause the same issues.
MXE & Cocaine
- Stimulants taken with MXE can lead to hypermanic states much more easily, especially if sleep is avoided.
MXE & Caffeine
- No likely interactions.
MXE & Alcohol
- There is a high risk of memory loss, vomiting and severe ataxia from this combination.
MXE & GHB\GBL
- Both substances cause ataxia and bring a risk of vomiting and unconsciousness. If the patient falls unconscious while under the influence there is a severe risk of vomit aspiration if they are not placed in the recovery position.
MXE & Opioids
- This combination can potentiate the effects of the opioid.
MXE & Tramadol
MXE & Benzodiazepines
- Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. Place affected patients in the recovery position to prevent vomit aspiration from excess.
MXE & MAOIs
MXE & SSRIs
- Depending on the SSRI this combination can be unpredictable.
DXM & Nitrous
DXM & Amphetamines
- Both substances raise heart rate, in extreme cases, panic attacks caused by these drugs have led to more serious heart issues.
DXM & MDMA
DXM & Cocaine
- Both substances raise heart rate, in extreme cases, panic attacks caused by these drugs have led to more serious heart issues.
DXM & Caffeine
- High doses of caffeine may cause anxiety which is less manageable when tripping, and since both are stimulating the combination may cause some physical discomfort.
DXM & Alcohol
- Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. Place affected patients in the recovery position to prevent vomit aspiration from excess. Additionally CNS depression can lead to difficulty breathing. Avoid on anything higher than 1st plateau.
DXM & GHB\GBL
- Both substances cause ataxia and bring a risk of vomiting and unconsciousness. If the patient falls unconscious while under the influence there is a severe risk of vomit aspiration if they are not placed in the recovery position. This combination is hard to predict.
DXM & Opioids
- CNS depression, difficult breathing, heart issues, hepatoxic, just very unsafe combination all around. Additionally, there is a reverse cross tolerance between opiates/dxm. I.E. if one takes dxm, their tolerance of opiates goes down slightly, thus causing additional synergistic effects.
DXM & Tramadol
DXM & Benzodiazepines
- Small doses of benzos can end a bad trip, but both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and this can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position.
DXM & MAOIs
- High risk of serotonin syndrome.
DXM & SSRIs
- High risk of serotonin syndrome.
Nitrous & Amphetamines
Nitrous & MDMA
Nitrous & Cocaine
Nitrous & Caffeine
Nitrous & Alcohol
- This combination can lead to vomiting.
Nitrous & GHB\GBL
Nitrous & Opioids
Nitrous & Tramadol
Nitrous & Benzodiazepines
Nitrous & MAOIs
Nitrous & SSRIs
Amphetamines & MDMA
- Amphetamines increase the neurotoxic effects of MDMA.
Amphetamines & Cocaine
- This combination of stimulants will increase strain on the heart. It is not generally worth it as cocaine has a mild blocking effect on dopamine releasers like amphetamine.
Amphetamines & Caffeine
- This combination of stimulants is not generally necessary and may increase strain on the heart, as well as potentially causing anxiety and greater physical discomfort.
Amphetamines & Alcohol
- Drinking on stimulants is risky because the sedative effects of the alcohol are reduced, and these are what the body uses to gauge drunkenness. This typically leads to excessive drinking with greatly reduced inhibitions, high risk of liver damage and increased dehydration. They will also allow you to drink past a point where you might normally pass out, increasing the risk. If you do decide to do this then you should set a limit of how much you will drink each hour and stick to it, bearing in mind that you will feel the alcohol and the stimulant less. Extended release formulations may severely impede sleep, further worsening the hangover.
Amphetamines & GHB\GBL
- Stimulants increase respiration rate allowing a higher dose of sedatives. If the stimulant wears off first then the opiate may overcome the patient and cause respiratory arrest.
Amphetamines & Opioids
- Stimulants increase respiration rate allowing a higher dose of opiates. If the stimulant wears off first then the opiate may overcome the patient and cause respiratory arrest.
Amphetamines & Tramadol
- Tramadol and stimulants both increase the risk of seizures.
Amphetamines & Benzodiazepines
Amphetamines & MAOIs
Amphetamines & SSRIs
MDMA & Cocaine
- Cocaine blocks some of the desirable effects of MDMA while increasing the risk of heart attack.
MDMA & Caffeine
- Caffiene is not really necessary with MDMA and increases any neurotoxic effects from MDMA.
MDMA & Alcohol
- Both MDMA and alcohol cause severe dehydration. Approach this combination with caution, moderation and sufficient hydration.
MDMA & GHB\GBL
MDMA & Opioids
MDMA & Tramadol
- Tramadol and stimulants both increase the risk of seizures.
MDMA & Benzodiazepines
MDMA & MAOIs
MDMA & SSRIs
Cocaine & Caffeine
- Both stimulants, risk of tachycardia, hypertension, and in extreme cases heart failure.
Cocaine & Alcohol
- Drinking on stimulants is risky because the sedative effects of the alcohol are reduced, and these are what the body uses to gauge drunkenness. This typically leads to excessive drinking with greatly reduced inhibitions, high risk of liver damage and increased dehydration. They will also allow you to drink past a point where you might normally pass out, increasing the risk. If you do decide to do this then you should set a limit of how much you will drink each hour and stick to it, bearing in mind that you will feel he alcohol less. Cocaine is potentiated somewhat by alcohol by reduction of cocaine breakdown which results in increased risk to the heart.
Cocaine & GHB\GBL
- Stimulants increase respiration rate allowing a higher dose of sedatives. If the stimulant wears off first then the opiate may overcome the patient and cause respiratory arrest. Likewise the G can wear off and leave a dangerous concentration of cocaine behind.
Cocaine & Opioids
- Stimulants increase respiration rate allowing a higher dose of opiates. If the stimulant wears off first then the opiate may overcome the patient and cause respiratory arrest.
Cocaine & Tramadol
- Tramadol and stimulants both increase the risk of seizures.
Cocaine & Benzodiazepines
Cocaine & MAOIs
Cocaine & SSRIs
- Risk of serotonin syndrome, Likely to make the SSRI's innefective with regular cocaine use. The SSRIs may also make the cocaine less effective. Mental stability and cocaine don't go together.
Caffeine & Alcohol
Caffeine & GHB\GBL
Caffeine & Opioids
Caffeine & Tramadol
Caffeine & Benzodiazepines
Caffeine & MAOIs
Caffeine & SSRIs
Alcohol & GHB\GBL
- Even in very low doses this combination rapidly leads to memory loss, severe ataxia and unconsciousness. There is a high risk of vomit aspiration while unconscious.
Alcohol & Opioids
- Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. Place affected patients in the recovery position to prevent vomit aspiration from excess. Memory blackouts are likely.
Alcohol & Tramadol
- Heavy CNS depressants, risk of seizures. Both substances potentiate the ataxia and sedation caused by the other and can lead to unexpected loss of consciousness at high doses. Place affected patients in the recovery position to prevent vomit aspiration from excess. Memory blackouts are likely.
Alcohol & Benzodiazepines
- Ethanol ingestion may potentiate the CNS effects of many benzodiazepines. The two substances potentiate each other strongly and unpredictably, very rapidly leading to unconsciousness. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position. Blacking out and memory loss is almost certain.
Alcohol & MAOIs
- The chemical tyramine in alcoholic beverages can have dangerous reactions with MAOIs, causing an increase in blood pressure.
Alcohol & SSRIs
- Alcohol may potentiate some of the pharmacologic effects of CNS-active agents. Use in combination may result in additive central nervous system depression and/or impairment of judgment, thinking, and psychomotor skills.
GHB\GBL & Opioids
- The two substances potentiate each other strongly and unpredictably, very rapidly leading to unconsciousness. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position.
GHB\GBL & Tramadol
- The sedative effects of this combination can lead to dangerous respiratory depression.
GHB\GBL & Benzodiazepines
- The two substances potentiate each other strongly and unpredictably, very rapidly leading to unconsciousness. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position.
GHB\GBL & MAOIs
- No study, but MAO B inhibitors should enhance the effects, no interaction with MAO A.
GHB\GBL & SSRIs
Opioids & Tramadol
- Concomitant use of tramadol increases the seizure risk in patients taking other opioids. These agents are often individually epileptogenic and may have additive effects on seizure threshold during coadministration. Central nervous system- and/or respiratory-depressant effects may be additively or synergistically present.
Opioids & Benzodiazepines
- Central nervous system and/or respiratory-depressant effects may be additively or synergistically present. The two substances potentiate each other strongly and unpredictably, very rapidly leading to unconsciousness. While unconscious, vomit aspiration is a risk if not placed in the recovery position Blackouts/memory loss likely.
Opioids & MAOIs
- Coadministration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) with certain opioids has been associated with rare reports of severe and fatal adverse reactions. There appear to be two types of interaction, an excitatory and a depressive one. Symptoms of the excitatory reaction may include agitation, headache, diaphoresis, hyperpyrexia, flushing, shivering, myoclonus, rigidity, tremor, diarrhea, hypertension, tachycardia, seizures, and coma. Death has occurred in some cases.
Opioids & SSRIs
Tramadol & Benzodiazepines
- Central nervous system- and/or respiratory-depressant effects may be additively or synergistically present. Vomit aspiration a risk when passed out, lay down in recovery position if ingested.